VECTOR-BORNE DISEASES [CSEC BIOLOGY & CSECHSB]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
CSEC HSB
- [D12] explain the effect of vectors on human health;
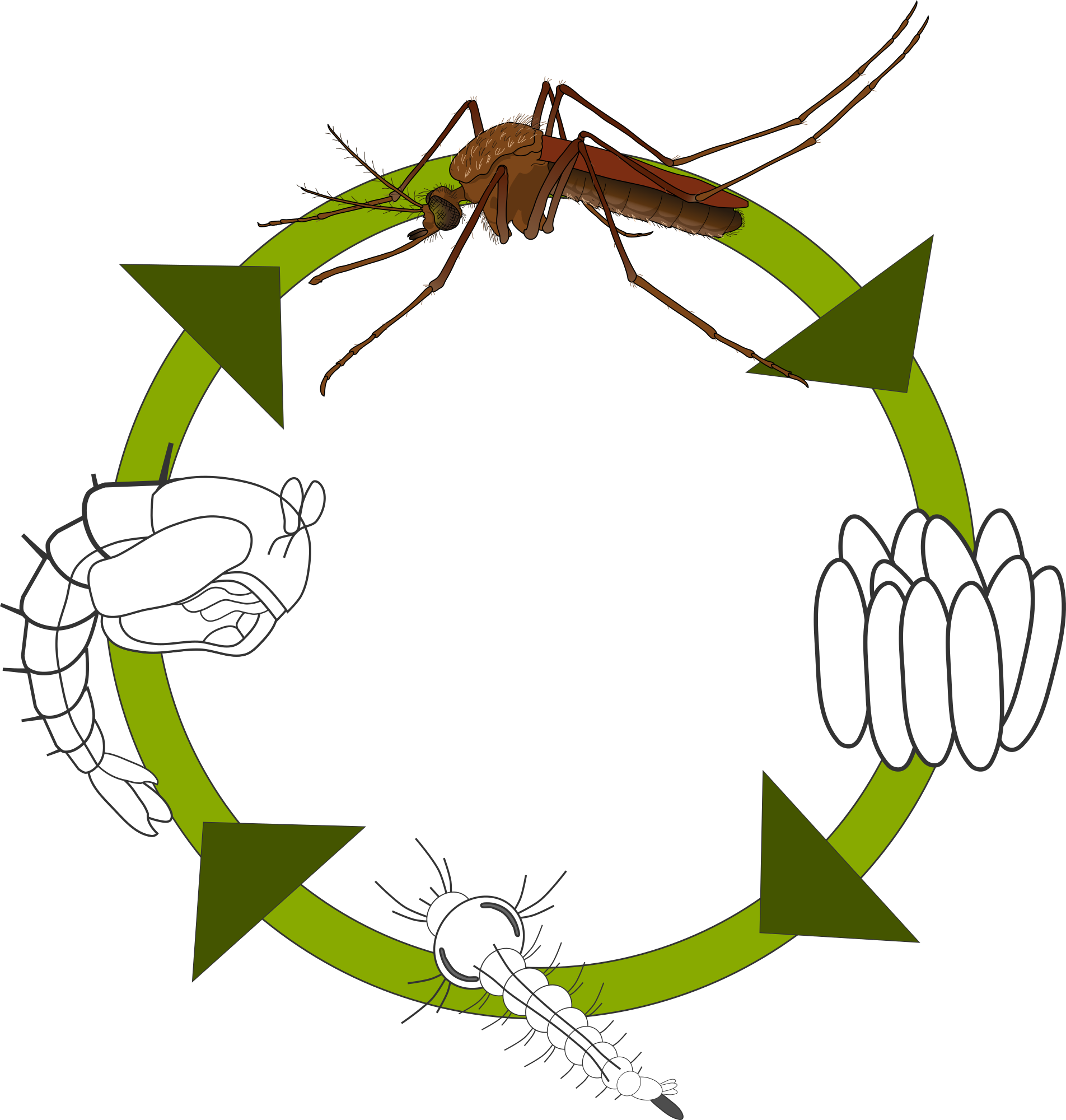
- [D13] describe the life cycle of the mosquito and housefly;
- [D14] discuss mosquito-borne diseases;
- [D15] explain the importance & methods of controlling vectors that affect human health.
CSEC BIOLOGY
- [B10.2] identify the stages in the life cycle of a mosquito;
- [B10.3] discuss the role of the mosquito as a vector in the transmission of pathogenic diseases;
- [B10.4] suggest appropriate methods of control of each stage of the life cycle of the mosquito;
DEFINITIONS
Vector-borne disease
These are infectious diseases that are transmitted by a vector.
Vector
An organism that carries pathogens in or on its body, and transmits the pathogens from one host to another. The vector is usually not harmed by the pathogen.
 |
| Vectors & The Diseases They Spread |
MALARIA
DENGUE FEVER
ZIKA
Zika's Medical Impact
The virus can be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her fetus.
Infected infants may be born with a much smaller head than is usual, because the brain does not develop fully. This is known as microcephaly.
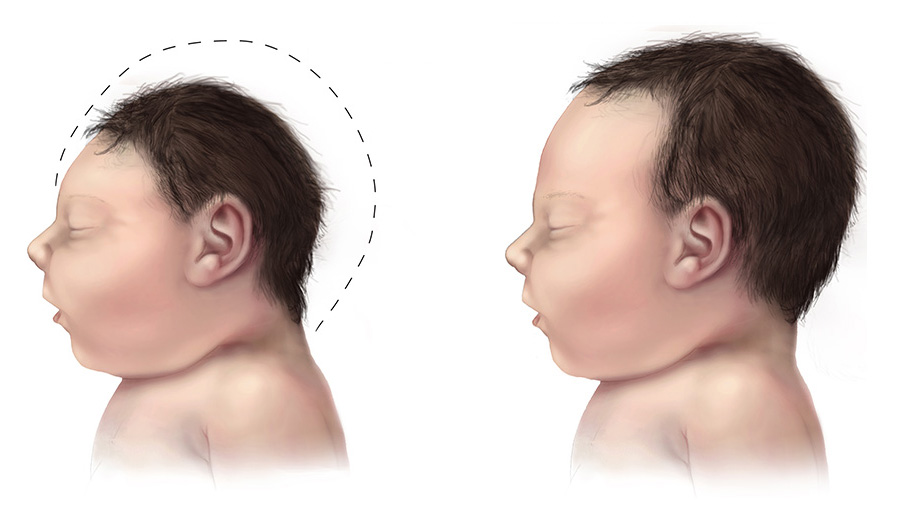 |
| Side-view Illustration of a Baby with Microcephaly (left) Compared to a Baby with a Typical Head Size |
There may be other congenital malformations, known as congenital Zika syndrome. There is also an increased risk of other pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage and premature birth.
In adults and older children, infection increases the risk of some conditions caused by nerve damage.
CHIKUNGUNYA
Chikungunya's Medical Impact
Severe joint pain usually lasts a few days but can persist for months, or even years.
Serious complications & death are rare. If it occurs, it is usually associated with other existing health problems, especially in elderly persons.
Main complications leading to death included:
- Inflammation of heart muscle
- Septic shock
- Inflammation of the brain
- Respiratory disorders
LEPTOSPIROSIS
Mosquito
The Mosquito as Vector
Humans are the primary hosts of the pathogens that are transmitted by mosquitoes. Mosquitoes are the secondary hosts.
Method of Transmission
- When a female mosquito bites an infected person, she sucks up blood that contains the pathogen.
- The pathogens pass through the walls of the intestines and move into her salivary glands.
- When she bites another person, she injects saliva into their blood, in order to prevent blood clotting.
- The pathogens are transmitted to that person with her saliva.
Housefly
.png/640px-Life_Cycle_of_the_House_Fly%2C_extracted_from_Flies_of_public_health_importance_and_their_control_(1976).png) |
The Housefly as Vector
Houseflies transmit several pathogens that cause food poisoning while they are feeding.
It feeds saprophytically. This means it releases digestive enzymes onto its food externally, then sucks up the digestive products through its proboscis.
Method of Transmission
- Houseflies collect pathogens on their legs, body and mouthparts, as well as taken into the guy while feeding.
- They then transfer these pathogens onto human food while walking on the food, feeding, vomiting or in their faeces.
CONTROLLING VECTORS
This is very important to control the spread of vector transmitted diseases.
Studying the life cycle of these vectors helps to guide development of strategies. These strategies will focus on one or more stages of the cycle.
Knowledge of the stages of the life cycle also helps disease control professionals to decide which strategy will be easiest, cheapest and/or most effective.
Controlling Mosquitoes
Eggs to Pupae
- Drainage of all areas of standing water (eggs to pupae).
- Addition of insecticides to breeding areas, to kill larvae & pupae.
- Introduce fish to breeding areas to feed on the larvae & pupae [biological control].
- Spraying oil on the surface of standing water. Prevents the larvae & pupae from breathing.
Adults
- Use of insecticides.
- Removal of dense vegetation, which removes the adult's shelter & protection.
Controlling Houseflies
- Properly dispose of human & animal waste.
- Cover food, so flies cannot land on them.
- Spray adults with insecticides.
- Use fly traps, to kill adults.
- Treat all sewage.
Controlling Rats
- Use traps and/or bait to kill them.
- Introduce cats or other animals that prey on rats [biological control].
- Rodent proofing of buildings [exclusion/mechanical strategy]