DRUG ABUSE [CSEC HSB]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
CSEC HSB
- [D22] discuss the use & misuse of drugs;
- [D23] explain the social effects of drug misuse on the individual, family, and community;
- [B2.11] discuss the effects of smoking.
- [B7.8] discuss the physiological, social and economic effects of drug abuse.
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS
Drug
- Any chemical that alters the way the body works by affecting metabolism.
- Some drugs can alter a person's psychological state and change their behavior.
Drug Abuse
- Taking drugs in excess or for non-medical reasons, so that they cause mental and/or physical harm.
- It often causes social problems because it affects relationships and can lead to crime.
Drug Dependence (aka 'Addiction)
 |
| Reasons People Give For Taking Drugs |
SOCIAL & ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF ILLEGAL DRUGS
Family Life
- Having a family member that is addicted to drugs severely disrupts family life.
- The unpredictable mood changes, restlessness and money problems of the addict puts a strain on the other members of the family and disrupts the peace of the home.
- The family home can start to feel like a war zone.
- Parents and siblings etc. can often feel helpless in the face of their addicted child or relative.
Crime
Drug dealers are criminals, and often members of a larger criminal organisation.
- They often target vulnerable people, and manipulate them to become addicted, so that they have have to buy drugs (guaranteed customer).
- The competition among dealers leads to corruption, gang warfare, and murder, affecting the whole community.
Economy
- Millions of dollars are spent annually on medical care for conditions caused by substance abuse, such as drug overdose.
- Rehabilitation is also costly, though it is worthwhile if it returns an addict to being a healthy, contributing member of society.
- Significant financial costs from policing & prosecuting crimes associated with drug misuse & abuse (robbery, gang warfare etc...)
- Those that work with hangovers cannot work to full potential. This leads to decreased productivity, from the local business to the entire economy.
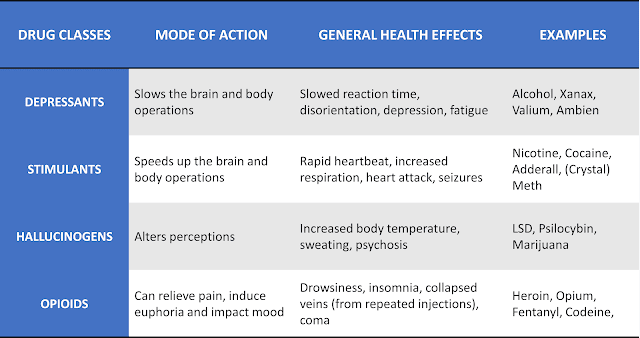
A CLOSER LOOK AT VARIOUS DRUGS
MARIJUANA
Marijuana's Effects on the Brain
Short-Term Effects
There are parts of the brain that have high numbers of brain cell receptors to natural chemicals that resemble THC. Marijuana over-activates these parts of the brain, as THC acts on these receptors.
It produces several of the following effects within an hour of smoking or ingesting marijuana:
- altered senses (for example, seeing brighter colours)
- altered sense of time
- changes in mood
- impaired body movement
- difficulty with thinking and problem-solving
- impaired learning and memory
- psychosis
- hallucinations (when taken in high doses)
- delusions (when taken in high doses)
Long-Term Effects
Other Health Effects of Marijuana
- Breathing problems - the smoke irritates the lungs, so marijuana smokers have similar breathing issues as tobacco smokers. These include:
- daily cough and phlegm
- more frequent lung illness
- higher risk of lung infections
- Lung illnesses - recently, serious lung illnesses and deaths have been connected to vaping THC oil, which is sometimes added to nicotine liquid in vaping devices. Public health experts are advising teens to stop using vaping products, especially if bought off the street.
- Increased heart rate - heart rate is raised for up to 3 hours after smoking. This increases the chance of a heart attack, especially in older persons and those with heart problems.
- Problems with child development during and after Pregnancy -
- Exposure to marijuana while still in the womb is associated with increased risk of problems with attention, memory, and problem-solving
- Marijuana use during pregnancy has been linked to low birth weight and a higher risk of preterm births
- With regular use of marijuana, THC in the breast milk can reach levels that could affect the baby's developing brain
Addiction
9 - 30% of marijuana users will develop a dependent relationship with the drug, with a smaller percentage going on to full addiction.If a person starts using the drug before the age of 18, they are 4-7 times more likely to develop a dependency.
Mental Effects
Long-term marijuana use has been linked to mental illness in some people, such as:
- temporary hallucinations and psychosis
- temporary paranoia and psychosis
- worsening symptoms in persons with schizophrenia
TOBACCO
Tobacco's & Nicotine's Effect on the Brain
Other Health Effects
- Toxins are released that can lead to lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema
- Smoking increases the risk of heart disease, which can then lead to stroke and heart attack
- Smoking has been linked to leukemia and other cancers, cataracts, and pneumonia
- Pregnant women who smoke run an increased risk of miscarriage, stillborn or premature infants
- Exposure to secondhand smoke has been linked to the following, in adults and/or children:
- coughing, phlegm, reduced lung function, pneumonia and bronchitis
- (children in particular) ear infections, severe asthma, lung infections and death from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Addiction
- irritability
- problems paying attention
- trouble sleeping
- increased appetite
- powerful cravings for tobacco
- depressed mood
OPIOIDS
How Do Opioids Affect the Brain?
These drugs attach to and activate opioid receptors located in many areas of the brain, spinal cord, and other organs in the body. Many of these receptors are associated with feelings of pain and pleasure.
Health Effects of Opioid Use
Short Term
They relieve pain and make people feel relaxed. It also causes these harmful effects:
- extreme drowsiness
- confusion
- nausea
- constipation
- slowed breathing
- insomnia
- muscle pain
- heart problems
- pneumonia
- addiction
- overdose
COCAINE
This is a powerfully addictive stimulant made from the leaves of the coca plant, native to South America.
How Does Cocaine Affect the Brain?
It increases the level of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain, in circuits related to control of movement, habitual behaviours and reward. It does so by preventing the dopamine from being recycled and reabsorbed back into the cell. As a result, it builds up to large amounts in the synaptic cleft between neurons, stopping their regular communication.
This flood of dopamine in the brain's reward circuit strongly reinforces drug-taking behaviours, because the reward circuit eventually adapts to the excess of dopamine. This leads to persons taking stronger doses more frequently to get the same high and relief from withdrawal.
Cocaine's Effect on Health
Short-Term Effects
Taking cocaine produces the following mental & psychological effects:
- Extreme happiness and energy
- Mental alertness
- Irritability
- Paranoia (extreme and unreasonable distrust of others)
Large amounts of cocaine can lead to bizarre, unpredictable, and violent behaviour.
Meanwhile, a cocaine 'high' produces the following physical effects:
- constricted blood vessels
- dilated pupils
- nausea
- raised body temperature and blood pressure
- fast or irregular heartbeat
- tremors and muscle twitches
- restlessness
Long-Term Effects
- Taking this drug decreases appetite, and can eventually cause malnourishment
- It has been linked to movement disorders, including Parkinson's disease
- In those that snort the drug:
- loss of smell
- nosebleeds
- frequent runny nose
- problems with swallowing
- In those that smoke the drug (crack):
- cough
- asthma & respiratory distress
- higher risk of infections such as pneumonia
- In those that take the drug orally:
- severe bowel decay from reduced blood flow
- In those that use needle injections:
- higher risk of contracting HIV, hepatitis C, and other bloodborne diseases
- skin and soft tissue infections
- scarred or collapsed veins
Addiction
Repeated use of cocaine can cause long-term changes in the brain's reward & other circuits, which then can lead to addiction.
- depression
- fatigue
- increased appetite
- unpleasant dreams & insomnia
- slowed thinking