HEALTH & DISEASE 101 [CSEC Biology & HSB]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
CSEC HSB
- [D1] define the terms good health and disease;
- [D2] classify the types of diseases;
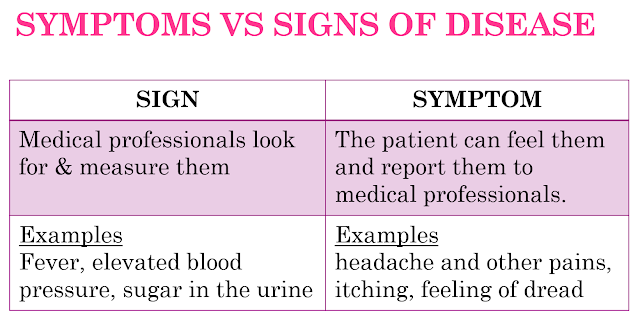
- [D3] differentiate between the terms signs and symptoms;
CSEC Biology
- [B10.1] distinguish among pathogenic, deficiency, hereditary, and physiological diseases;
- [B10.5] discuss the treatment and control of the four main groups of disease;
- [B10.6] discuss the social, environmental, and economic implications of disease with reference to both plant and animal diseases.
WHAT IS HEALTH?
WHO Definition (1946)
"A state of complete physical, mental, and social well being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity."
Physical Health
- All the body's systems are functioning properly
- A person with good physical health can have an active life with no issues
Mental Health
- Has to do with one's state of mind
- A person with good mental health...
- Are free of disorders such anxiety or depression
- Can cope with the stresses and strains of life
Social Health
- Has to do with how we interact with others
- A person with good social health...
- Has good relationships with family, friends, work and/or school colleagues
- Copes well when meeting strangers
WHAT IS DISEASE?
- It is any change from normal health
- Part(s) of the body is not functioning efficiently
DISEASE CLASSIFICATION
The broadest categories are based on whether the cause is another living organism (pathogen) or not.
Communicable Diseases
- Aka Infectious Disease or Pathogenic Disease.
- Caused by a pathogen, which is a microorganism (or worm) that invades the body.
- These pathogens develop a parasitic relationship with the invaded organism.
- Disease symptoms and signs develop that are characteristic of the particular pathogen, and the type of tissue or organ it focuses on.
- Examples: influenza, fungal infections, and malaria
Infectious disease can be classified according to:
- how the pathogen enters the body or whether it establishes itself on the skin's surface
- the organ system that is predominantly affected.
Non-Communicable Diseases
- These diseases CANNOT be passed from one person to another, as they are not caused by pathogens.
- The following are types of non-communicable diseases. Each is a category of disease in itself.