FOOD TESTS [CSEC BIOLOGY & HSB]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
HSB
[B1.5] perform tests to distinguish among food nutrients;
CSEC BIOLOGY
[B2.6] perform tests to distinguish among food substances;
STARCH TEST - IODINE TEST
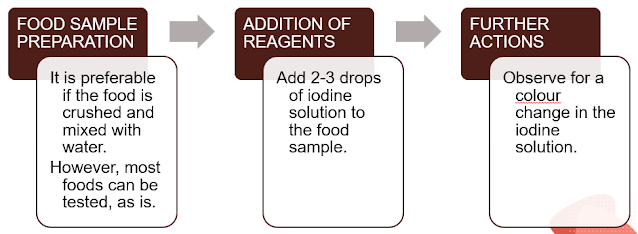 |
| IODINE TEST PROCEDURE |
If starch is present the iodine solution changes colour from yellow-brown to blue-black.
 |
| IODINE TEST - POSITIVE & NEGATIVE RESULTS |
SIMPLE, REDUCING SUGARS - BENEDICT'S TEST
 |
| BENEDICT'S TEST PROCEDURE FOR SIMPLE, REDUCING SUGARS |
If simple sugars are present, the Benedict's solution in the reaction mixture will undergo a colour change.
Depending on the concentration of sugar in the sample, the colour change will differ.
Green (lowest) < Yellow < Orange < Brick red (highest)
Benedict's solution changes colour due to a reduction reaction. (A reduction reaction involves the removal of oxygen atoms from a chemical compound.)
As a result, the sugars that produce this result are called REDUCING SUGARS.
COMPLEX, NON-REDUCING SUGARS - MODIFIED BENEDICT'S TEST
 |
| MODIFIED BENEDICT'S TEST PROCEDURE |
The boiling with acid hydrolysed the complex sugar, which broke it down to its simple sugar components.
Once sugar is present, one gets the same result as for simple sugars, with the same range of colours according to concentration.
PROTEIN - BIURET TEST
 |
| BIURET TEST PROCEDURE |
If soluble proteins are present in the food sample, the reaction mixture will change colour from blue to pink-violet.
 |
| POSITIVE VS NEGATIVE RESULTS FOR BIURET TEST |
 |
| IDEAL POSITIVE RESULT FOR BIURET TEST |
LIPIDS - GREASE-SPOT OR EMULSION TEST
If lipids are present, the following occurs:
- Grease spot: a translucent spot on the paper remains after being left to dry
- Emulsion test: the reaction mixture forms a cloudy emulsion after mixing.




