CONTRACEPTION & FAMILY PLANNING [CSEC HSB & BIOLOGY]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
CSEC BIOLOGY
[B9.5] discuss the advantages and disadvantages of various methods of birth control.
CSEC HSB
- [B7.7] explain how birth control methods prevent pregnancy;
- [B7.8] discuss the advantages and disadvantages of birth control methods;
- [B7.9] discuss the issues related to abortion;
- [B7.10] discuss the importance of family planning.
WHY IS CONTRACEPTION IMPORTANT?
- Too rapid population growth can put a strain on a country's resources.
- Having children too early, and/or without having other aspects of life in order can put a strain on a young couple.
- Too many children, especially if spaced too closely, can cause major physical health issues for the mother, and places many challenges on a young family.
- It can be used in a family that has decided not to have anymore children before the mother goes into menopause.
BENEFITS OF FAMILY PLANNING AT A SOCIETAL LEVEL
Improves Maternal Health & Child Survival Rates
Avoiding pregnancy too early, too late, or too often benefits mothers and their children. Delaying pregnancy reduces rates of maternal mortality. A 3-year interval between births lowers the rate of infant and child mortality.
Reduces the Number of Abortions, Especially Unsafe Abortions
Empowers Women
Women who can control the number and timing of their children can take better advantage of education and economic opportunities, improving their own future and that of their families.
Promotes Social & Economic Development, and Security
High population growth hampers poor countries' economic development as their expanding population competes for limited resources such as food, housing, schools and jobs. Rapid and unsustainable populations render societies more unstable, which can lead to civil unrest.
Protects the Environment
A rapidly growing population exacerbates environmental degradation and strains the world's resources.
TYPES OF BIRTH CONTROL
There are many forms of birth control, of varying reliability.
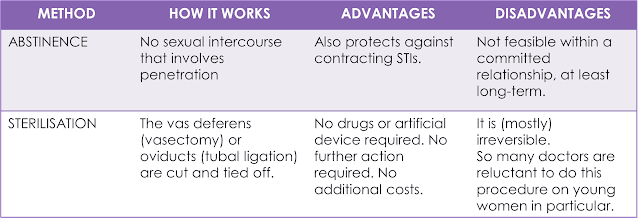
Highly Reliable Birth Control
Reliable Birth Control
Low-Reliability Birth Control
ABORTION
It can either be surgical or non-surgical. The latter involves the use of abortifacient pharmaceutical drugs to induce the abortion.
It is illegal in some Caribbean countries, though the laws vary in terms of how strict the ban on abortion is. Where abortion is illegal, is still occurs. Women that can afford it can get a safe abortion, though in secret. Women that cannot afford it may go to extreme (and unsafe) lengths to terminate a pregnancy.
Dangers of Illegal Abortions
These abortions are generally unsafe, being carried out in unhygienic conditions by an unskilled practitioner. It therefore carries many health risks for the mother.
These risks range from infection and future infertility to heavy bleeding and death.
On average, 4,000 women a year die from unsafe, illegal abortions in the Caribbean.
The Ethical Issues Surrounding Abortion
Abortion is one of the most difficult and controversial moral topics in today's society. Many people view abortion as murder of unborn children. On the other hand, some people view free access to safe abortions as a right for women.
Another argument that is usually advanced against abortion is that the fetus is an innocent person, separate from the mother, and with its own right to life. There are those, however, that argue that a foetus cannot be considered a person with the full rights that go with it. They point out the possible legal and other ramifications of taking that position. For example, a pregnant woman would be considered two separate people under law, which would impact many aspects of life outside of abortion.
Caribbean Policy and Law Concerning Abortion
Legislation varies widely across the Caribbean. Even in countries where abortion is illegal, exceptions are made in a wide range of instances, such as:
- to preserve the life of the mother
- if the mother was a victim of rape or incest
- in the case of fetal abnormality
- to protect the mental or physical health of the woman.