MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM [CSEC HSB & BIOLOGY]
SYLLABUS REFERENCE
CSEC HSB
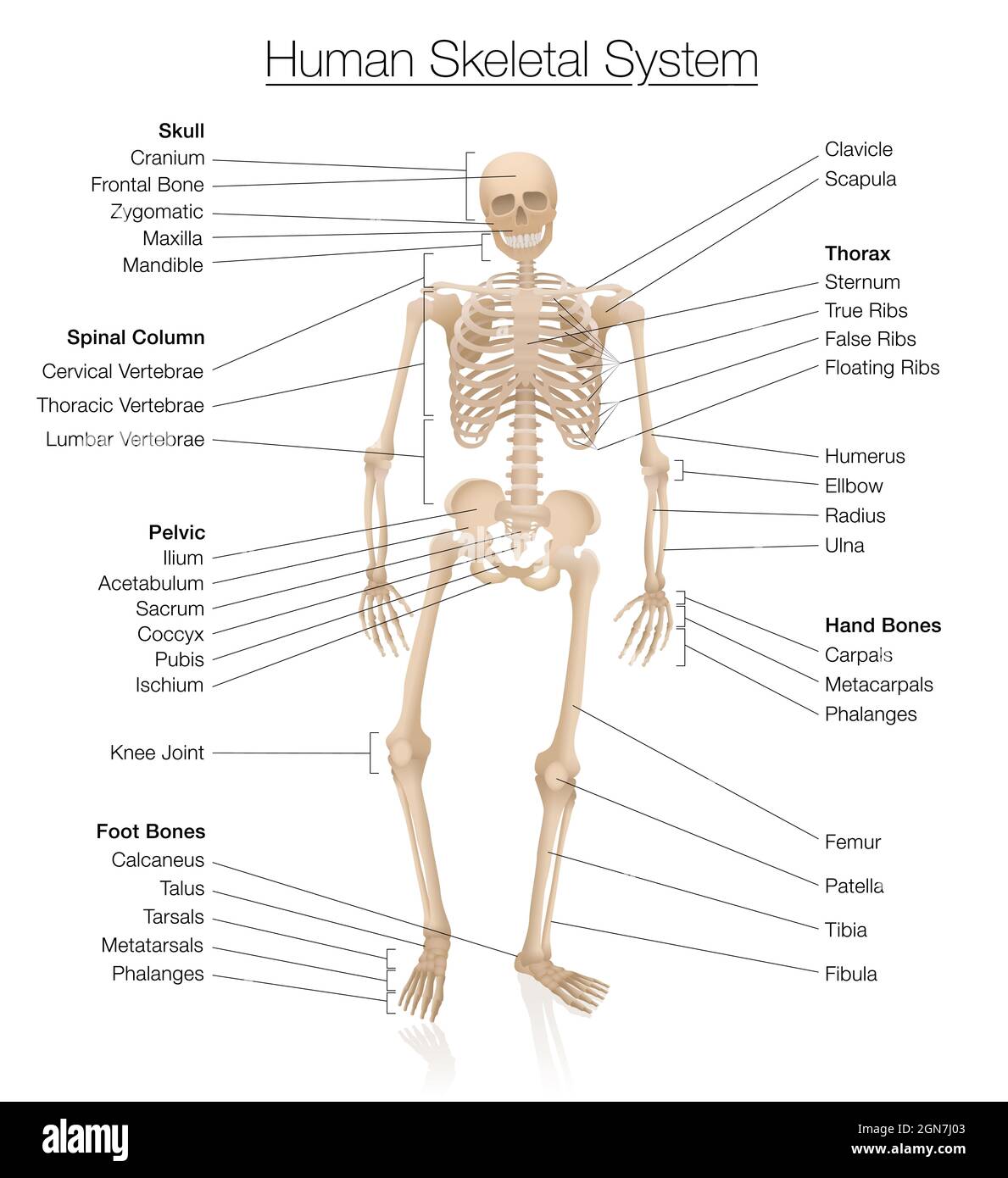
- [B4.1] identify the major bones of the skeleton;
- [B4.2] relate the structure of the skeleton to its functions;
- [B4.7] identify a hinge joint, fixed joint, and ball-and-socket joint;
- [B4.9] identify the biceps and triceps of the upper arm;
- [B4.10] explain how skeletal muscles function in the movement of a limb;
- [B4.11] explain the importance of locomotion to man.
CSEC Biology
- [B6.2] relate the structure of the skeleton to its function in humans;
- [B6.3] discuss the importance of locomotion in animals;
- [B6.4] describe the mechanism of movement in a human forelimb.
IMPORTANCE OF LOCOMOTION TO HUMANS
Locomotion is the ability to more the entire individual from one place to another independently.
This ability is very important to our independence and identity.
Generally, locomotion is required:
- for defence
- to search for food and shelter
- to care for young ones
- to work
COMPONENTS OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
The Skeleton
The skeleton has a basic framework that consists of the following:
- Axial Skeleton
- Appendicular Skeleton
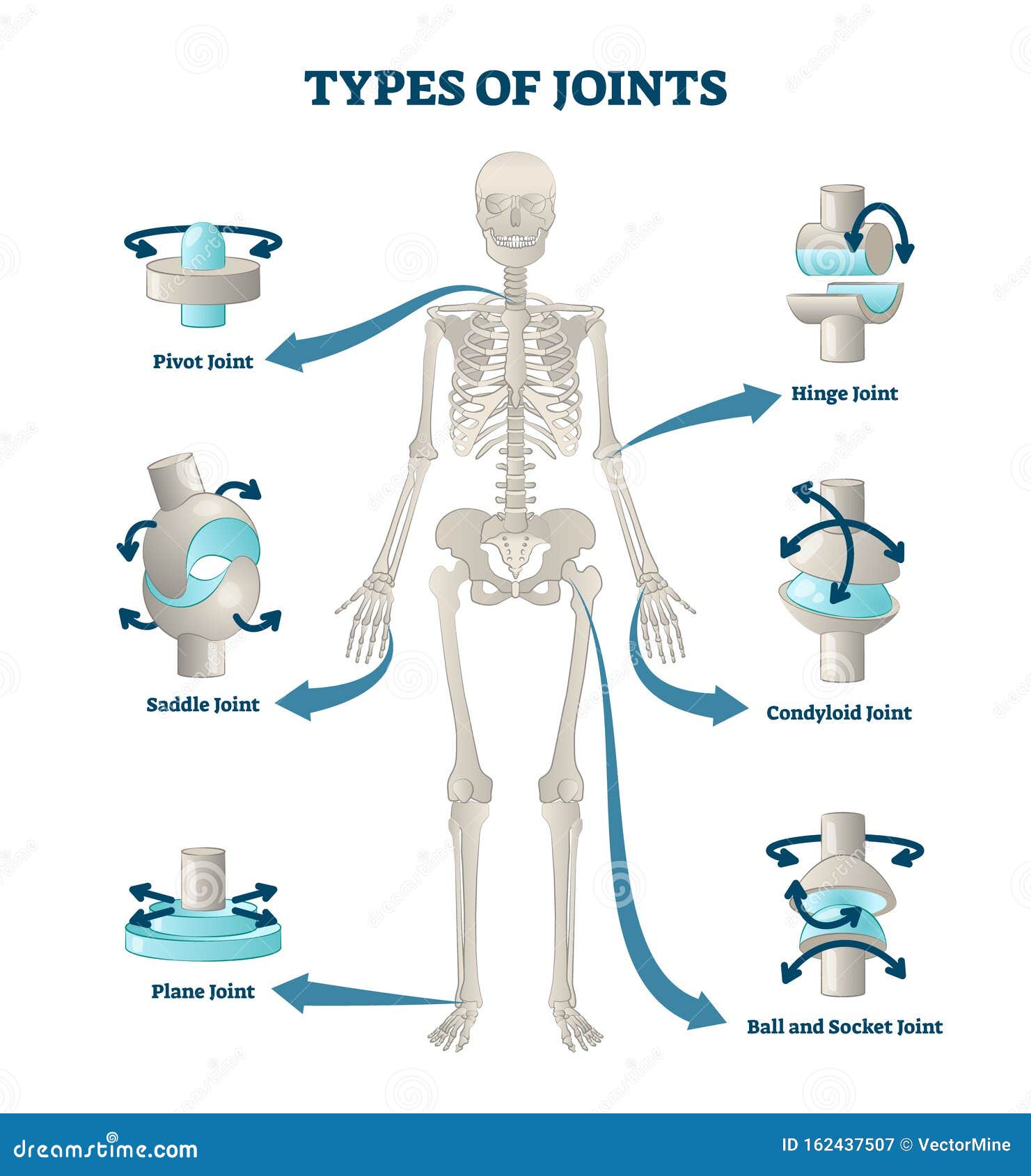
Types of Joints
At CSEC level, the focus is on the following types of joints...
Hinge
Fixed
Ball-and-Socket
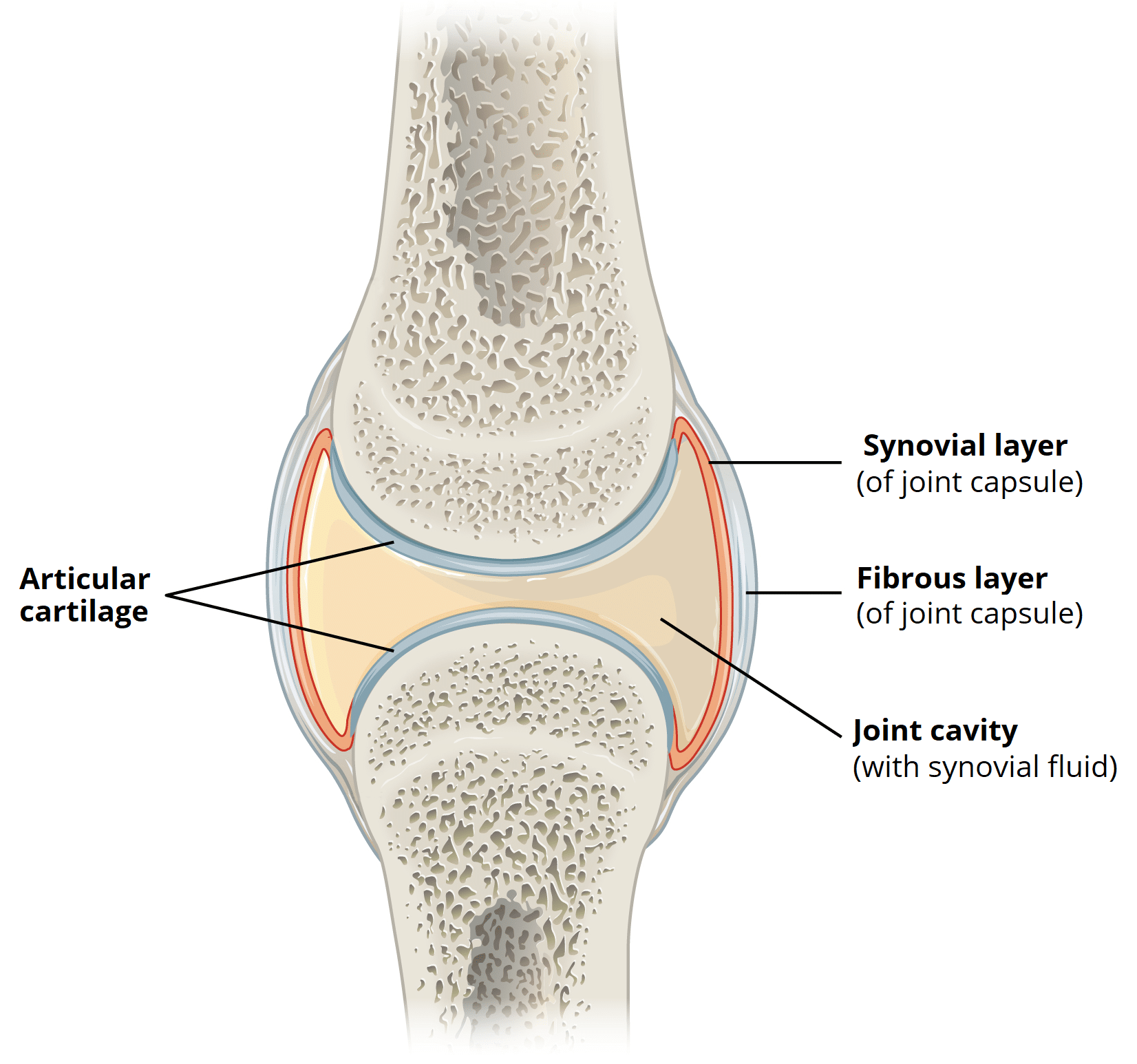
Both hinge and ball-and-socket joints are SYNOVIAL JOINTS.
Functions of the Skeleton
Movement
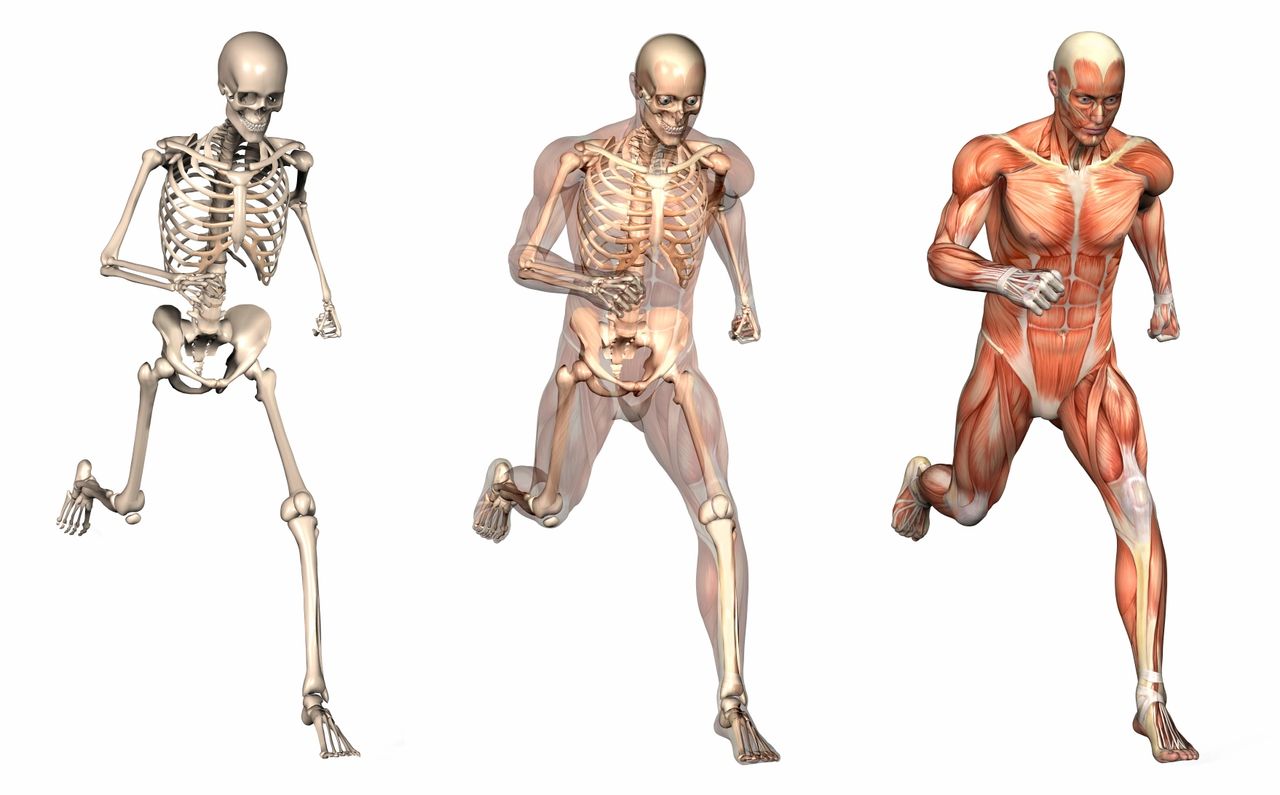
Bones act as points of attachment for the skeletal muscles. The skeleton acts as a system of levers, powered by muscular contraction.
Protection
- The cranium protects the brain, eyes, and ear canal.
- The rib cage protects the lungs and heart.
- The vertebral column protects the spinal cord.
- The pelvis protects the uterus (womb).
Support
The skeleton acts as a framework (or scaffolding) for the rest of the organ systems of the body.
The backbone supports the limbs and head. The jawbones support the teeth.
Breathing
The intercostal muscles move the rib cage up and down, in and out, in order to facilitate breathing.
This movement increases and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing air to move in and out of the lungs.
Production of Red Blood Cells
Red bone marrow, found on the inside of short bones and at the ends of long bones such as the humerus, have stem cells.
These special cells divide by mitosis to produce red blood cells, thus continuously replacing the older cells.
Important Comparisons
MECHANICS OF MOVEMENT
- Muscles can only contract.
- The bones act as levers and points of attachment.
- Each arrangement consists of two or more bones, plus muscles are arranged to pull the bone in opposite directions. These are called antagonistic muscles.